Deep learning and KPU basic knowledge
What can I learn after reading this chapter?
- Understand some basic content of deep learning
- Understand the characteristics of KPU inside K210
- Understand the problems that may be encountered during the use of KPU and the solutions to the problems
Overview
In this chapter, we will introduce some basic knowledge of deep learning and K210 internal KPU, as well as the problems that you are likely to encounter in this part. Deep learning and the application examples it covers are a very large field, and no one can make it clear with a document. I hope that this document can give you a certain understanding of deep learning, and if there is a problem beyond the description of this document, you can solve the problem through search engine queries and other means.
About Deep Learning
Before introducing deep learning, let's first introduce neural networks.
What is a neural network? It is an algorithmic mathematical model that imitates the behavioral characteristics of animal neural networks and performs distributed parallel information processing.
Below, let us give a simple example to illustrate what it does.
In fact, to some extent, when we were in elementary school, we had already begun to use neural network-related ideas to solve practical problems. At this time, you may be full of question marks QAQ. Don't be afraid, let me come one by one. Now, suppose there is an equation y = kx + b. I believe you must have seen this equation countless times. In fact, we can regard this equation as the "model" of the neural network, the unknown "k" as the weight of the neural network, and "b" as the bias of the neural network. At this time we need to train this neural network model. In fact, the training process is the process of solving the global optimal weights and biases on the data set. At this time, suppose this equation satisfies "x=1, y=2", "x=2, y=4". This satisfying condition is the data set mentioned above. Through the training of this network in the human brain, we can know that the optimal weight of the entire network is 2, and the optimal bias is 0. At this point, the training of the neural network is completed.
However, it is worth mentioning that the ultimate goal of training is always prediction. Throughout the ages, so many neural networks have consumed a lot of computing resources to find suitable weights and biases. All are to be able to find a correspondence between input data and output data. For an excellent neural network, its input data should be random and uncertain (not trained in the data set). The output data is accurate and reliable. Going back to the above, we trained the neural network "y = 2x + 0". At this time, the data x in the dataset is "1" and "2". At this time, in order to evaluate the performance of the model, we input the non-data set data "3". At this time, through the neural network forward propagation, the output value "6" is obtained. So far, the prediction of the neural network model is completed.
I used a very simple demo to explain what the neural network is doing. Let's take a look at the real neural network model.
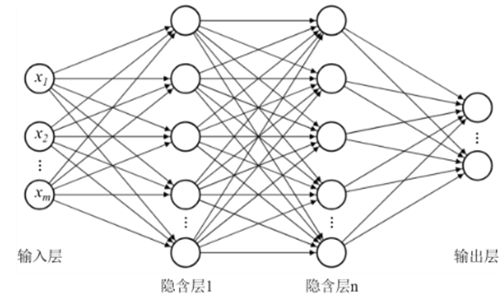
The above picture shows a more common fully connected neural network model (Fully connected neural network). Comparing this network structure with the previous "y = 2x + 0" network, we can find the following differences:
- The number of input data is uncertain (there can be n inputs)
- The number of output data is uncertain (there can be n outputs)
- The number of parameters is uncertain (there can be n fully connected layers in the figure, and each layer can contain n neurons, resulting in the number of parameters being n)
The model construction process can be regarded as the process of determining the number of parameters (when the network layer structure is determined, the number of parameters is also determined), and the model training process can be regarded as the process of determining the global optimal parameters on the data set. The prediction process of the model can be regarded as the process of input data * parameter = prediction result. (*Represents some kind of calculation)
After having a certain understanding of neural networks, deep learning will be introduced next. You can think of deep learning as an improved neural network algorithm. The relationship between it and several other terms is: machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence, and deep learning and neural networks are a subset of machine learning.
The difference between neural network and deep learning, as well as the advantages of deep learning, etc., due to limited space, can not be introduced here. If you are interested, you can query through search engines.
About KPU
The K210 SOC is equipped with a KPU (Neural Network Processor), which is a general neural network processor, which can realize convolutional neural network calculations with low power consumption, and always obtain the size, coordinates and type of the detected target. Detect and classify faces or objects.
The KPU on the K210 has the following features:
- Support fixed-point models trained by mainstream training frameworks according to specific restriction rules
- There is no direct limit to the number of network layers, and each layer of convolutional neural network parameters can be configured separately, including the number of input and output channels, input and output row width and column height
- Support two convolution kernels 1x1 and 3x3
- Support any form of activation function
- The maximum supported neural network parameter size is 5.5MiB to 5.9MiB when working in real time
- The maximum supported network parameter size during non-real-time work is (Flash capacity-software volume)
The internal structure of KPU is shown in the figure below.
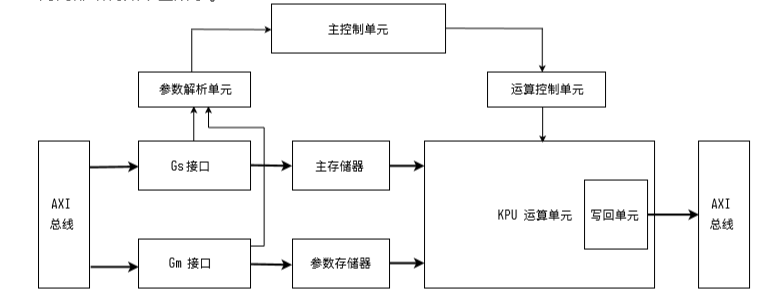
You can click here to view related APIs and Demos of KPU under Maixpy.
Common problems in the use of KPU
1. What size model can KPU load?
When k210 runs c code, it can load about 6MB model.
When running maixpy (mini), a model of about 3MB can be loaded.
When running maixpy (full version), a model of about 2MB can be loaded.
2. What model can be loaded and run by KPU?
The kmodel converted by nncase can be loaded and run by kpu.
Click here for nncase instructions
nncase tflite ops support click here
Click here for nncase frequently asked questions
3. How can KPU load the model?
Load the model in the TF card
kpu.load("/sd/test.kmodel")Load the model in Flash
kpu.load(offset)The offset here is the offset address of the model in the flash. The model can be burned into the internal flash of the k210 through k-flash
4. What should I do if an error "memory overflow" is reported?
This problem is generally caused by the model being too large. You can try the following solutions in turn:
- Change the firmware of maixpy mini version
- Perform model pruning optimization
- Abandon the development under maixpy firmware, and use Kanzhi C SDK for development.
5. What should I do if the error "load error, only support kmodel v3/v4" is reported?
If this problem occurs, you can try the following solutions:
- If loading the model in the flash, please make sure that the flash offset is filled in correctly and that there is no conflict with the maixpy firmware.
- If it is kmodel V4 converted using nncase 0.2.0, please try to convert using nncase 0.1.0 to generate kmodel V3. (As of 2020/06/30, the loading bug of kmodel v4 by maixpy has not been fixed yet)
6. I want to select and load different models (for example, press the button to run the target classification, press the button again to run the target detection), how should I write the program?
Because of the limited flash, it is recommended to load all k210 models into the TF card. Because the internal RAM is limited, before switching between different models for kpu.load(k210model), please execute kpu.deinit(k210model) to release the model in SRAM. Otherwise it will report an error "memory overflow".



 English
English Translate
Translate